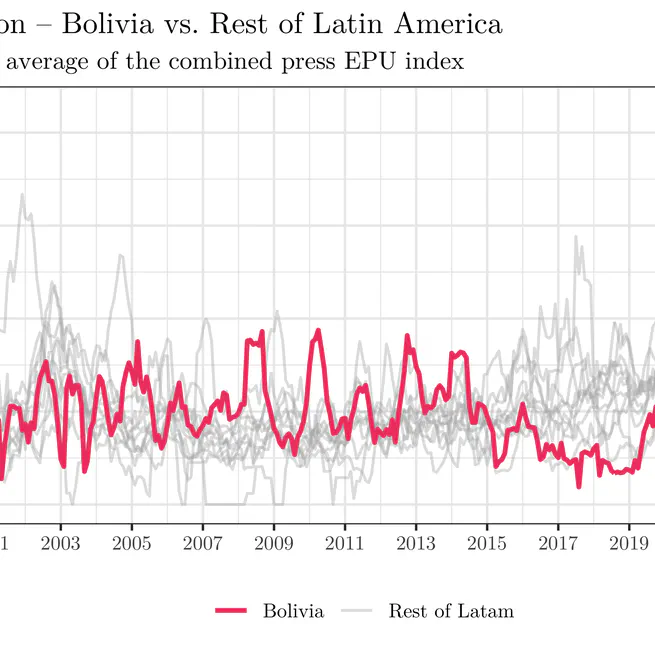
In this post I analyze the Economic Policy Uncertainty (EPU) Index recently published for Bolivia and other Latin American countries by the Bank of Spain. Using these data, I explore the recent evolution of economic uncertainty in Bolivia, its comparison with the rest of the region, and its possible relationship with recent political events. The results suggest that Bolivia remains among the countries with relatively high levels of uncertainty, reinforcing the importance of predictable economic policies and institutional frameworks based on clear rules. Reducing discretion in public policy can help strengthen economic confidence and create more favorable conditions for investment and growth.
Feb 4, 2026
As demand for reproducible macroeconomic analysis grows, manually extracting data from international organizations becomes a bottleneck: processes are poorly documented, non-scalable, and difficult to automate. SDMX —the statistical standard adopted by the IMF, ECB, OECD, World Bank, and others— offers a structured solution that makes it possible to find, understand, and extract data consistently through APIs. This post provides a practical introduction to how the SDMX model works, how to identify dataflows, structures, and codelists, and how to build reproducible queries in both XML and JSON. Using examples from the IMF (WEO) and the ECB (€STR), it shows a generalizable workflow for automating macroeconomic series in R, culminating with the use of the imfapi package, which abstracts much of the technical complexity.
Dec 7, 2025
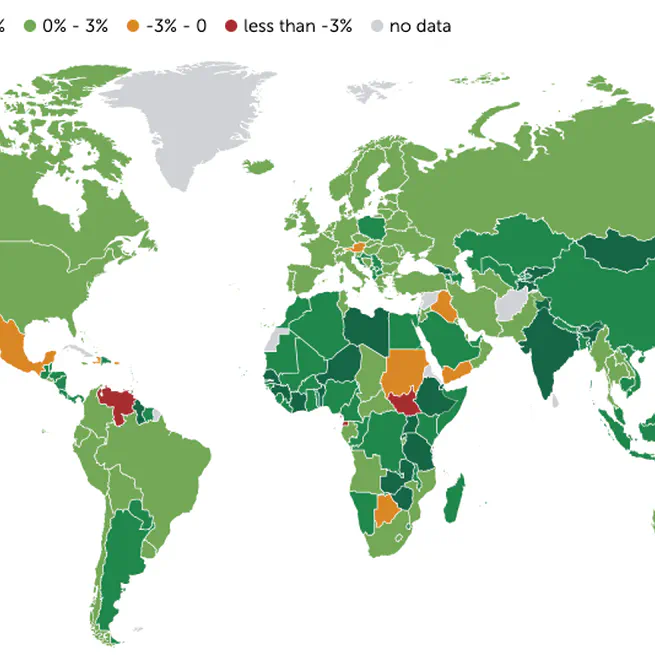
This article shows how to extract economic data from the IMF using its DataMapper API, with `R` functions to organize and analyze information on indicators and countries. Applications are illustrated with Bolivia and Spain, demonstrating how to access structured data such as GDP growth, unemployment, inflation, fiscal balance, and public debt.
Sep 29, 2025
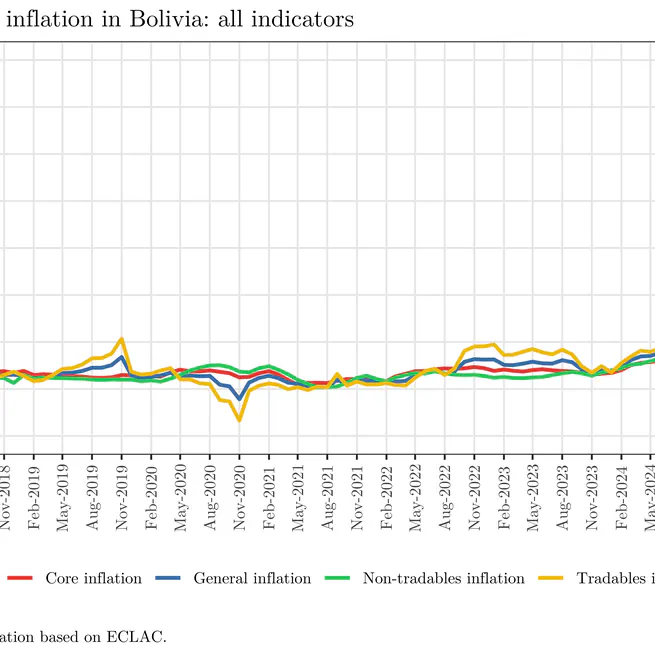
This article explores data extraction from ECLAC and its application to the analysis of inflation in Bolivia, using the R programming language to access relevant economic data. As of August 2025, Bolivia’s year-on-year inflation ranges from 16.05% (non-tradable goods) to 30.43% (tradable goods).
Sep 20, 2025